PERT/CPM is effective tool for project planning. PERT stands for critical path method. Even though these techniques were develop for defence applications they are useful for many maintenance projects. The conventional "Bat Chart" as given below is adequate for a small straight forward jobs having around 200 activities. But for larger maintenance projects such as plant shut down and overhaul jobs where activities are many PERT/CPM techniques help us to ascertain the logistics of different resources.
Any maintenance project consists of number of activities. These activities are represented in a network by arrows.
ACTIVITY is clearly definable task to which a know quantity of resources will be applied and hence activities always take time. An activity is represented by an arrow.
DUMMY ACTIVITY are used to indicate a constraint and keep the logic correct or sometimes numbering system unique. Dummy activity are represented by broken arrow.
EVENT is the junction of arrow(s) and as such does not consume time. It represents that point of time when all activities ending at that point are done and all succeeding activities that begin at that point can start. It is represented by a circle.
INTERDEPENDENCY of activities indicate relationship between different activities.
For any project, the first event represents the starting point and the last event represents the completion point of a project. Example:
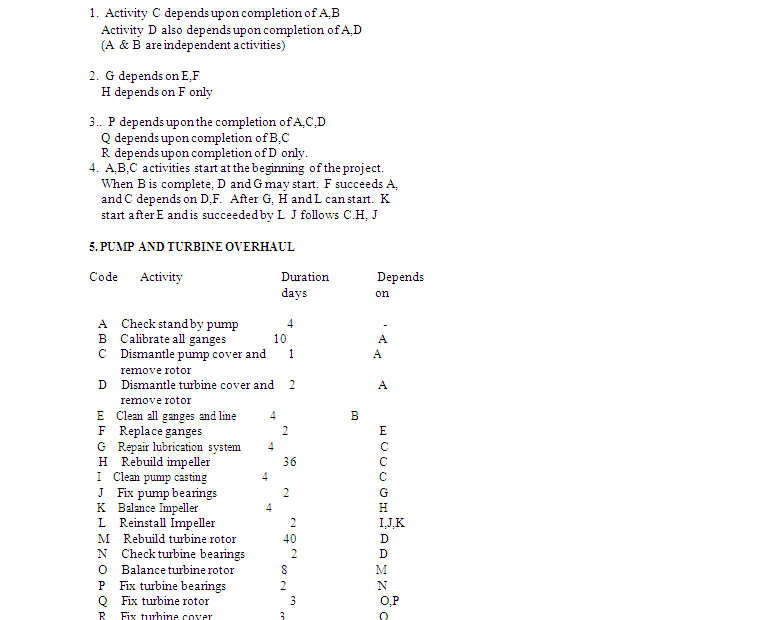
After the project has been divided into activities and the inter-dependencies have been established the network can be drawn. The activity elapsed timings are to be estimated simultaneously. At this stage the effect of holidays and vacations are excluded. Normally the time estimates are given by the maintenance engineers and industrial engineers. Single time estimates are possible for some activities where uncertainty exists in certain activities such as reconditioning. Assembly, Procurement of parts etc. the activity durations are decided based three time estimates
Time Analysis computations can be grouped under two types
Project Duration
- Forward pass calculations
- Backward pass calculations
Float analysis
The forward pass computations decides the earliest time at which a particular activity can start or can completed, assuming that the project starts at Zeroeth time. As an activity cannot start until all its preceding activities are completed the early start is given by the highest of the early completion times of the proceeding activities. The backward pass computations decides the latest time at an activity can be allowed to be started/completed without affecting the project duration.
The above computations help us to find out the expected project completion time. For intermediate activities also the completion timings can be found out.
Slack or float signifies the free times available for an activity or event in the net work. Whenever the late completion time of an activity has more free time the project as a whole would not be delayed. If the early and late completion time are the same for an activity if means that there is no slack or free time. Such activities are called critical activities. For all the activities falling in the critical path the float is zero.
The network technique is basically a management tool. In addition to finding out the project duration the technique is can be used for planning and scheduling, cost optimisation and also resource allocation.
PERT/CPM